Teacher Materials
Student Activity
Student
Assessment
Learning
Goals/Standards
STELLA Versions
- isee Player software
- Right-click to download the models
- Vensim PLE Software
- Right-click to download the models
Web-based Simulation

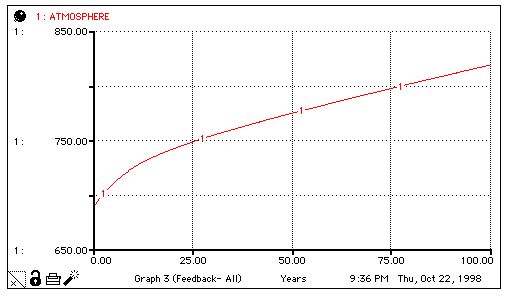
INIT ATMOSPHERE = 690
MARINE(t) = MARINE(t - dt) + (M_Photo - M_Res - M_Death) *dt
INIT MARINE = 7
M_DEAD_ORGANIC(t) = M_DEAD_ORGANIC(t - dt) + (M_Death - M_Decomp) *dt
INIT M_DEAD_ORGANIC = 3000
TERRESTRIAL(t) = TERRESTRIAL(t - dt) + (T_Photo - T_Res - T_Death) *dt
INIT TERRESTRIAL = 450
T_DEAD_ORGANIC(t) = T_DEAD_ORGANIC(t - dt) + (T_Death - T_Decomp) *dt
INIT T_DEAD_ORGANIC = 700
FOSSIL_FUELS(t) = FOSSIL_FUELS(t - dt) + (- Emissions) *dt
INIT FOSSIL_FUELS = 10000
T_Res = 23*(TERRESTRIAL/450)
T_Photo = 48*(ATMOSPHERE/690)
T_Decomp = 25*(T_DEAD_ORGANIC/700)
T_Death = 25*(TERRESTRIAL/450)
M_Res = 5*(MARINE/7)
M_Photo = 35*(ATMOSPHERE/690)
M_Decomp = 30*(M_DEAD_ORGANIC/3000)
M_Death = 30*(MARINE/7)
Emissions = 5.5